The app world reaches across most countries in the world today. Each country has its own set of laws and regulations. This can make it difficult for foreign developers to distribute apps in other countries. On the Google Play side of things, the two countries with the most different of app regulations are Japan and South Korea.
Providing addition account information:
There is some additional account information that you have to add to your app listing if you want your app to appear in Japan and Korea. For Japan, you only need to provide the additional information if your app is paid or has in-app purchases. On the Korean Play Store, all developers need to provide additional information.
To comply with Japanese and Korean law, you need to provide users with contact information for your app. This includes the name, phone number and address of someone who works for your app. In Korea, if you are an individual developer, not a business, you only have to provide a phone number. You can easily add the name, address and phone number of a point-of-contact person for your app through your Play Console.
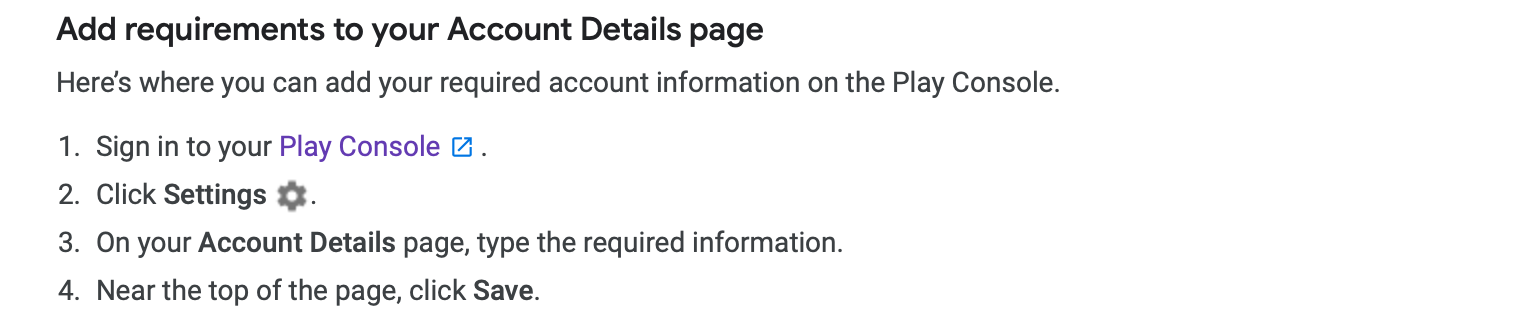
This allows users to contact you if they have any issues with your app. As an alternative, you can provide a web address that contains your contact information.
Note: This information applies if you are distributing a paid app or have in-app purchases in Japan. In Korea, any app distributed on the Play Store needs contact information. If your app is paid or has in-app purchases, you also have to provide your business registration number, e-commerce license number and the name of the agency that issued the e-commerce license.
Other Korean requirements:
The requirements to list your app on the Play Store in Korea are a little more extensive than Japan. There are three main boxes that all developers have to check.
Korean Game Rating and Administrative Committee:
The GRAC reviews games and is the licensing authority in Korea. If your game is considered to be 18+, then it can only be published on the Play Store in Korea with GRAC’s permission. There are five content categories that GRAC looks at when reviewing games: sexuality, violence, crime and drugs, improper language and gambling. You can learn more about GRAC from their site.
Korean Ministry of Gender Equality & Family:
MOGEF is in charge of content regulations that relate to gender equality, family and kids. If your app is designated as “harmful to juveniles”, then you have to verify the age and name of users before allowing them access to mature content. Google has implemented an age verification system in Korea that requires users to verify their age and name. If your app is compliant with Google Play developer policies, but still flagged as “harmful to juveniles”, then users will still be able to access your app. Check out MOGEF’s site to learn more.
Korean Communications Commission:
The KCC implements broadcasting and telecommunication regulations in Korea. In order for an app to collect location-based information from Korean users, you need to have a license from KCC. Once you receive a KCC license for location-based services, you have to provide the KCC the details of how you’re using location. As a developer, it’s your responsibility to get permission from Korean users to collect location information. Visit KCC’s site if you need more information.
Especially as a foreign developer, being aware of the local laws and requirements in a country for apps is extremely important. The last thing you want to happen is have your app kicked off the Play Store. In Korea, 73.38% of smartphone users have an android, making the Play Store a huge market in the country. While only 29.91% of Japanese users have Android devices, that is still a significant market. Listing your app well in these countries — from both a legal and ASO standpoint — is highly important.




